라즈베리파이에 대해서 공부를 하면서 공부한 내용을 블로그에도 기록하고 있습니다.
스스로를 위한 기록이지만, 누군가에게 도움되는 내용이길 바라면서 블로그를 작성하고 있지만, 어느 정도 수준으로 작성해야 하는지 고민이 많이 됩니다.
왜냐하면, 이 글을 읽는 분들께서 어느 정도의 배경지식을 가지고 있고, 어느 정도의 수준인지 알기 어렵기 때문입니다.
Ubuntu Linux에 어느 정도 익숙하고, Samba Server에 대한 개념을 알고 계신다는 전제로 이 글을 작성하고자 합니다.
아주 간단히 설명을 드리자면, Samba Server는 Windows 공유폴더와 같은 개념이라고 보시면 될 것 같습니다.
PC 간에 파일을 주고받는 방법은 scp, ftp 등 여러 가지가 있겠지만, Host PC가 Windows일 경우 Target PC에 Samba Server를 구성하는 게 가장 편리한 것 같습니다.
본 페이지에서는 라즈베리파이 Ubuntu Linux에 Samba 서버를 설치하여, Host PC인 Windows에서 라즈베리파이를 공유폴더로 접근할 수 있도록 설정하는 방법에 대해서 기록하고자 합니다.
[작성자 환경]
제가 글을 작성하고 있는 환경은 아래와 같으므로 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- Hardware : Rapsberry Pi 4B (8GB)
- microSD Card : 4GB
- OS : Ubuntu Linux
[Samba 설치]
그럼 본격적으로 Samba 패키지를 설치하도록 하겠습니다.
터미널 실행 단축키인 Ctrl + Alt + T를 동시에 누르시면 터미널을 손쉽게 열 수 있습니다.
| $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get upgrade $ sudo apt-get install samba |
sudo apt-get install samba 명령을 통해서 samba 패키지를 설치합니다.
패키지 설치 전에는 항상 sudo apt-get update 명령과 sudo apt-get upgrade 명령을 미리 관용적으로 수행하는 습관을 들이시기 바랍니다. (이 과정은 다소 시간이 많이 걸릴 수 있습니다.)
설치가 완료되면 자동으로 samba server가 실행됩니다.
| $ sudo service smbd status |
● smbd.service - Samba SMB Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/smbd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2021-01-18 19:33:29 UTC; 8min ago
Docs: man:smbd(8)
man:samba(7)
man:smb.conf(5)
Main PID: 69660 (smbd)
Status: "smbd: ready to serve connections..."
Tasks: 4 (limit: 9258)
CGroup: /system.slice/smbd.service
├─69660 /usr/sbin/smbd --foreground --no-process-group
├─69664 /usr/sbin/smbd --foreground --no-process-group
├─69665 /usr/sbin/smbd --foreground --no-process-group
└─69670 /usr/sbin/smbd --foreground --no-process-group
Jan 18 19:33:11 ubuntu systemd[1]: Starting Samba SMB Daemon...
Jan 18 19:33:11 ubuntu update-apparmor-samba-profile[69654]: grep: /etc/apparmor.d/samba/smbd-shares: No such f>
Jan 18 19:33:11 ubuntu update-apparmor-samba-profile[69657]: diff: /etc/apparmor.d/samba/smbd-shares: No such f>
Jan 18 19:33:29 ubuntu systemd[1]: Started Samba SMB Daemon.
sudo service smbd status 명령을 통해서 samba daemon이 정상적으로 active 되어있는 것을 확인하였습니다.
[Samba 계정 추가]
Samba 계정을 추가하도록 하겠습니다.
라즈베리파이에 Ubuntu Linux를 설치하면 기본적으로 생성되는 ubuntu 계정을 이용하고자 합니다.
| $ sudo smbpasswd -a ubuntu |
물론 ubuntu가 아닌 다른 계정을 이용하시고 싶으시면 계정을 생성하시고 해당 계정을 smbpasswd -a 명령으로 추가하시면 됩니다.
[Samba Server 설정 파일 수정]
이번에는 Samba Server의 설정 파일을 수정하는 방법에 대해서 설명드리고자 합니다.
| $ sudo vi /etc/samba/smb.conf |
위와같이 입력하면 samba 설정 파일 내용이 나오는데, 다소 복잡하게 보일 수 있으나 쫄 필요는 없습니다.
대부분이 주석이고, 실제 설정 내용은 간결한 편입니다.
#
# Sample configuration file for the Samba suite for Debian GNU/Linux.
#
#
# This is the main Samba configuration file. You should read the
# smb.conf(5) manual page in order to understand the options listed
# here. Samba has a huge number of configurable options most of which
# are not shown in this example
#
# Some options that are often worth tuning have been included as
# commented-out examples in this file.
# - When such options are commented with ";", the proposed setting
# differs from the default Samba behaviour
# - When commented with "#", the proposed setting is the default
# behaviour of Samba but the option is considered important
# enough to be mentioned here
#
# NOTE: Whenever you modify this file you should run the command
# "testparm" to check that you have not made any basic syntactic
# errors.
#======================= Global Settings =======================
[global]
## Browsing/Identification ###
# Change this to the workgroup/NT-domain name your Samba server will part of
workgroup = WORKGROUP
# server string is the equivalent of the NT Description field
server string = %h server (Samba, Ubuntu)
#### Networking ####
# The specific set of interfaces / networks to bind to
# This can be either the interface name or an IP address/netmask;
# interface names are normally preferred
; interfaces = 127.0.0.0/8 eth0
# Only bind to the named interfaces and/or networks; you must use the
# 'interfaces' option above to use this.
# It is recommended that you enable this feature if your Samba machine is
# not protected by a firewall or is a firewall itself. However, this
# option cannot handle dynamic or non-broadcast interfaces correctly.
; bind interfaces only = yes
#### Debugging/Accounting ####
# This tells Samba to use a separate log file for each machine
# that connects
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
# Cap the size of the individual log files (in KiB).
max log size = 1000
# We want Samba to only log to /var/log/samba/log.{smbd,nmbd}.
# Append syslog@1 if you want important messages to be sent to syslog too.
logging = file
# Do something sensible when Samba crashes: mail the admin a backtrace
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
####### Authentication #######
# Server role. Defines in which mode Samba will operate. Possible
# values are "standalone server", "member server", "classic primary
# domain controller", "classic backup domain controller", "active
# directory domain controller".
#
# Most people will want "standalone server" or "member server".
# Running as "active directory domain controller" will require first
# running "samba-tool domain provision" to wipe databases and create a
# new domain.
server role = standalone server
obey pam restrictions = yes
# This boolean parameter controls whether Samba attempts to sync the Unix
# password with the SMB password when the encrypted SMB password in the
# passdb is changed.
unix password sync = yes
# For Unix password sync to work on a Debian GNU/Linux system, the following
# parameters must be set (thanks to Ian Kahan <<kahan@informatik.tu-muenchen.de> for
# sending the correct chat script for the passwd program in Debian Sarge).
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
passwd chat = *Enter\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *Retype\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *password\supdated\ssuccessfully* .
# This boolean controls whether PAM will be used for password changes
# when requested by an SMB client instead of the program listed in
# 'passwd program'. The default is 'no'.
pam password change = yes
# This option controls how unsuccessful authentication attempts are mapped
# to anonymous connections
map to guest = bad user
########## Domains ###########
#
# The following settings only takes effect if 'server role = primary
# classic domain controller', 'server role = backup domain controller'
# or 'domain logons' is set
#
# It specifies the location of the user's
# profile directory from the client point of view) The following
# required a [profiles] share to be setup on the samba server (see
# below)
; logon path = \\%N\profiles\%U
# Another common choice is storing the profile in the user's home directory
# (this is Samba's default)
# logon path = \\%N\%U\profile
# The following setting only takes effect if 'domain logons' is set
# It specifies the location of a user's home directory (from the client
# point of view)
; logon drive = H:
# logon home = \\%N\%U
# The following setting only takes effect if 'domain logons' is set
# It specifies the script to run during logon. The script must be stored
# in the [netlogon] share
# NOTE: Must be store in 'DOS' file format convention
; logon script = logon.cmd
# This allows Unix users to be created on the domain controller via the SAMR
# RPC pipe. The example command creates a user account with a disabled Unix
# password; please adapt to your needs
; add user script = /usr/sbin/adduser --quiet --disabled-password --gecos "" %u
# This allows machine accounts to be created on the domain controller via the
# SAMR RPC pipe.
# The following assumes a "machines" group exists on the system
; add machine script = /usr/sbin/useradd -g machines -c "%u machine account" -d /var/lib/samba -s /bin/false %u
# This allows Unix groups to be created on the domain controller via the SAMR
# RPC pipe.
; add group script = /usr/sbin/addgroup --force-badname %g
############ Misc ############
# Using the following line enables you to customise your configuration
# on a per machine basis. The %m gets replaced with the netbios name
# of the machine that is connecting
; include = /home/samba/etc/smb.conf.%m
# Some defaults for winbind (make sure you're not using the ranges
# for something else.)
; idmap config * : backend = tdb
; idmap config * : range = 3000-7999
; idmap config YOURDOMAINHERE : backend = tdb
; idmap config YOURDOMAINHERE : range = 100000-999999
; template shell = /bin/bash
# Setup usershare options to enable non-root users to share folders
# with the net usershare command.
# Maximum number of usershare. 0 means that usershare is disabled.
# usershare max shares = 100
# Allow users who've been granted usershare privileges to create
# public shares, not just authenticated ones
usershare allow guests = yes
#======================= Share Definitions =======================
# Un-comment the following (and tweak the other settings below to suit)
# to enable the default home directory shares. This will share each
# user's home directory as \\server\username
;[homes]
; comment = Home Directories
; browseable = no
# By default, the home directories are exported read-only. Change the
# next parameter to 'no' if you want to be able to write to them.
; read only = yes
# File creation mask is set to 0700 for security reasons. If you want to
# create files with group=rw permissions, set next parameter to 0775.
; create mask = 0700
# Directory creation mask is set to 0700 for security reasons. If you want to
# create dirs. with group=rw permissions, set next parameter to 0775.
; directory mask = 0700
# By default, \\server\username shares can be connected to by anyone
# with access to the samba server.
# Un-comment the following parameter to make sure that only "username"
# can connect to \\server\username
# This might need tweaking when using external authentication schemes
; valid users = %S
# Un-comment the following and create the netlogon directory for Domain Logons
# (you need to configure Samba to act as a domain controller too.)
;[netlogon]
; comment = Network Logon Service
; path = /home/samba/netlogon
; guest ok = yes
; read only = yes
# Un-comment the following and create the profiles directory to store
# users profiles (see the "logon path" option above)
# (you need to configure Samba to act as a domain controller too.)
# The path below should be writable by all users so that their
# profile directory may be created the first time they log on
;[profiles]
; comment = Users profiles
; path = /home/samba/profiles
; guest ok = no
; browseable = no
; create mask = 0600
; directory mask = 0700
[printers]
comment = All Printers
browseable = no
path = /var/spool/samba
printable = yes
guest ok = no
read only = yes
create mask = 0700
# Windows clients look for this share name as a source of downloadable
# printer drivers
[print$]
comment = Printer Drivers
path = /var/lib/samba/printers
browseable = yes
read only = yes
guest ok = no
# Uncomment to allow remote administration of Windows print drivers.
# You may need to replace 'lpadmin' with the name of the group your
# admin users are members of.
# Please note that you also need to set appropriate Unix permissions
# to the drivers directory for these users to have write rights in it
; write list = root, @lpadmin
우선 기존 설정 파일을 백업합니다.
| $ sudo mv /etc/samba/smb.conf /etc/samba/smb_default.conf |
선호하는 편집기를 열고 /etc/samba/smb.conf 파일을 생성하고 아래 내용을 붙여 넣습니다.
[global]
server string = %h server (Samba, Ubuntu)
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
max log size = 1000
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
server role = standalone server
obey pam restrictions = yes
unix password sync = yes
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
passwd chat = *Enter\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *Retype\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *password\supdated\ssuccessfully*
pam password change = yes
idmap config * : backend = tdb
usershare allow guests = yes
[ubuntu]
comment = Users profiles
path = /home/ubuntu
guest ok = no
create mask = 0600
writeable = yes
directory mask = 0700아래의 첨부파일을 바로 받으셔도 됩니다.
GitHub에도 해당 파일을 업로드 해두었습니다.
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/boyinblue/raspberry/main/samba/smb.conf
wget 명령을 통해서 받으셔서 편집하셔도 좋습니다.
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/boyinblue/raspberry/main/samba/smb.conf
[삼바 서비스 재시작]
| $ sudo service smbd restart |
삼바 서비스를 재시작합니다.
[삼바 서버 접속]
탐색기를 열고 \\192.168.25.2와 같이 라즈베리파이 주소를 입력하고 로그인을 시도해봅니다.

정상적으로 잘 로그인되는 것을 확인하였습니다.
[윈도우즈 자격증명으로 편리하게 로그인하는 방법]
윈도우즈 자격 증명을 추가해놓으면 이후부터는 ID, PW 입력 없이 자동으로 접속됩니다.
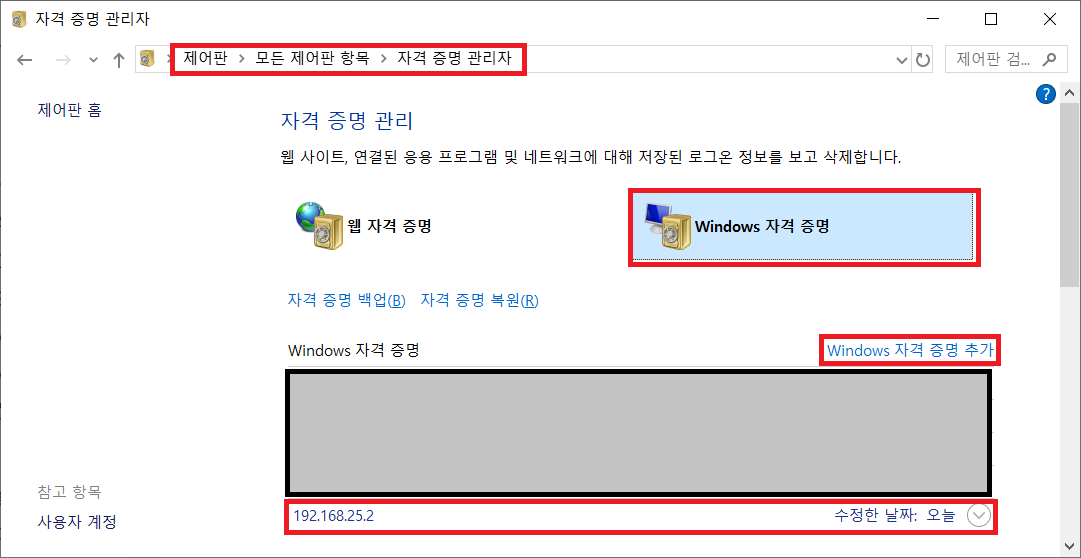
[포트번호]
만약 NAT 내부에 라즈베리파이가 존재하여 포트 포워딩이 필요하다면 아래의 포트들에 대해서 포트 포워딩을 하시기 바랍니다.
| Protocol | Port Number | Note |
| TCP | 139 | |
| 445 | ||
| UDT | 137 | |
| 138 |
[끝 맺음말]
이상으로 라즈베리파이에 Samba Server를 설정하는 방법에 대한 설명을 모두 마칩니다.
부디 유용한 정보였기를 바랍니다.
이상입니다.
'Study > 라즈베리파이 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [라즈베리파이] sudo: python: command not found 에러 발생시 조치방법 (0) | 2021.01.21 |
|---|---|
| [라즈베리파이] Ubuntu Linux에 FTP 서버 설치 (0) | 2021.01.20 |
| 라즈베리파이 회로도 & Data Sheet (0) | 2021.01.19 |
| [라즈베리파이] 발열 테스트 및 CPU 온도 확인 방법 (0) | 2021.01.19 |
| [라즈베리파이] 보드 시리얼번호 확인하는 방법 (0) | 2021.01.17 |


